地址:https://common-buy.aliyun.com/?spm=a2c4e.11155515.0.0.DjCjOv&commodityCode=cas#/buy
第一步:

第二步:
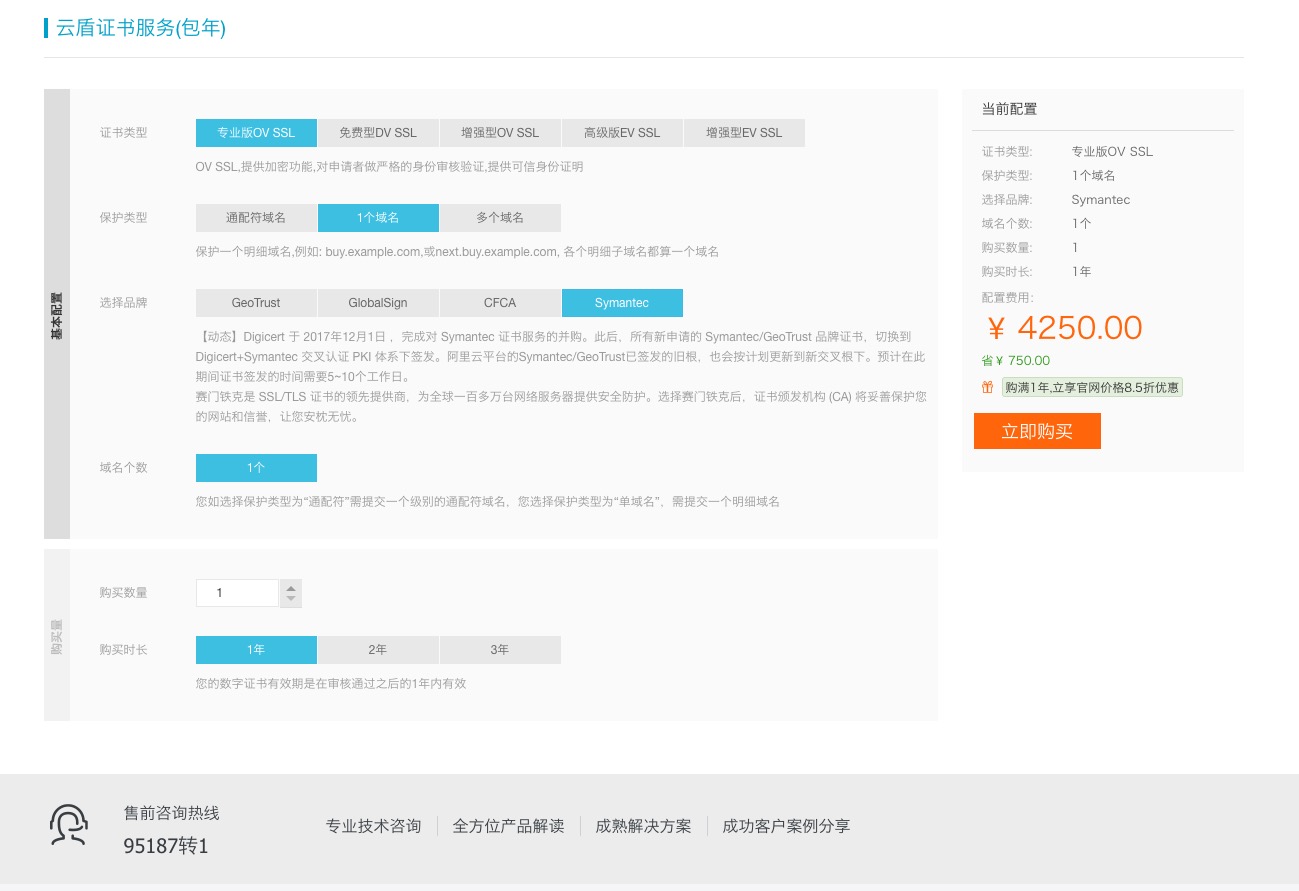
第三步:

第四步:点击证书控制台

第[……]
地址:https://common-buy.aliyun.com/?spm=a2c4e.11155515.0.0.DjCjOv&commodityCode=cas#/buy
第一步:

第二步:

第三步:

第四步:点击证书控制台

第[……]
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
const REGEX = /(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})T(\d{2}):(\d{2}):(\d{2})/ /** * @function format time * @param val, format * @return {string} * @example * <template> * <div> * <span>{{item.time | formatTime('yyyy/MM/dd hh:mm:ss')}}</span> * </div> * </template> * import {formatTime} from '../../library/timeFormat' * export default { * filters: {formatTime} * } */ export const formatTime = (val, format) => { if (val) { /** * @instructions 如果不是时间戳格式,且含有字符 '-' 则将 '-' 替换成 '/' && 删除小数点及后面的数字 * @reason 将 '-' 替换成 '/' && 删除小数点及后面的数字 的原因是safari浏览器仅支持 '/' 隔开的时间格式 */ if (val.toString().indexOf('-') > 0) { val = val.replace(/T/g, ' ').replace(/\.[\d]{3}Z/, '').replace(/(-)/g, '/') // 将 '-' 替换成 '/' val = val.slice(0, val.indexOf('.')) // 删除小数点及后面的数字 } let date = new Date(val) date.setHours(date.getHours() + 8) const [whole, yy, MM, dd, hh, mm, ss] = date.toISOString().match(REGEX) const year = new Date().getFullYear() const month = new Date().getMonth() + 1 const dates = new Date().getDate() if (format) { return format .replace('yyyy', yy) .replace('yy', yy.slice(2)) .replace('MM', MM) .replace('dd', dd) .replace('hh', hh) .replace('mm', mm) .replace('ss', ss) } else { return [yy, MM, dd].join('-') + ' ' + [hh, mm, ss].join(':') } } else { return '--' } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
例子: let cols = document.querySelectorAll('ul li') [].forEach.call(cols, function (col, index) { // TODO } 分析: ① []是一个空数组,无论这个数组里的最初值是什么,它们都不会被使用到; ② forEach方法是一个数组方法,只有数组才能调用;完整写法:Array.prototype.forEach,Array.forEach为简写; ③ call方法: 语法:fun.call(thisArg, arg1, arg2, ...) 参数:thisArg:在 fun 函数运行时指定的this值; arg1, arg2, ... : 指定的参数列表; 综上:[]这个空数组里的值(当然,它没有值)是最初的this值,通过call方法,当这个空数组调用方法forEach时, cols里的值会取代空数组原先的this值。 通俗的说,就是cols需要使用forEach这个方法, 但是这个方法是一个数组方法,只有数组才能调用,于是通过call方法来了个偷梁换柱, 在数组调用forEach方法的时候,将数组里的this值替换成了cols的值,达成了目的。 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 |
首先克隆:git clone https://github.com/facebook/WebDriverAgent.git 在执行命令: ./Scripts/bootstrap.sh 时报错: Please make sure that you have Carthage installed (https://github.com/Carthage/Carthage) Note: We are expecting that carthage installed in /usr/local/bin/ 安装carthage:brew install carthage 执行 ./Scripts/bootstrap.sh 仍报同样的错,再次安装carthage提示: Warning: carthage 0.27.0 is already installed, it's just not linked. You can use `brew link carthage` to link this version. 执行:brew link carthage 报: Linking /usr/local/Cellar/carthage/0.27.0... Error: Permission denied @ dir_s_mkdir - /usr/local/Frameworks 提权:sudo brew link carthage 报: Error: Running Homebrew as root is extremely dangerous and no longer supported. As Homebrew does not drop privileges on installation you would be giving all build scripts full access to your system. 原因可能是我刚把系统升级到 macOS High Sierra 10.13.2 搜到一大把解决方法: 1、sudo chown -R $(whoami) $(brew --prefix)/* 2、sudo chown -R $(whoami) /usr/local/* 3、brew upgrade 4、Uninstall Homebrew: /usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/uninstall)" Then re-install it: /usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)" 第四个没试,前三个都试了一遍,brew link carthage仍然报错,但是 ./Scripts/bootstrap.sh 可以执行了。 依赖安装完以后,双击WebDriverAgent.xcodeproj这个文件,会在Xcode中对应打开。 紧接着证书签名: 勾选 Automatically manage signing 然后选择Team 登录你的 Apple ID 下载证书。 在TARGETS里面选中WebDriverAgentLib: <img src="http://skillnull.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/131514876676_.pic_hd-1.jpg" alt="" width="1878" height="1057" /> 在TARGETS里面选中WebDriverAgentRunner: <img src="http://skillnull.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/141514876772_.pic_hd.jpg" alt="" width="1878" height="1057" /> 报错了,修改BundleID: <img src="http://skillnull.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/111514876450_.pic_hd.jpg" alt="" width="1878" height="1057" /> <img src="http://skillnull.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/121514876645_.pic_.jpg" alt="" width="626" height="19" /> <img src="http://skillnull.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/151514877046_.pic_hd.jpg" alt="" width="1878" height="1057" /> 报错解决。 接着在菜单栏中选择Product=>Destination=>你的手机,Product=>Scheme=>WebDriverAgentRunner,最后Product=>Test 运行。 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
Mac系统从10.12 macOS Sierra更新到10.13.2macOS High Sierra后执行git命令报错 xcrun: error: invalid active developer path (/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools), missing xcrun at: /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/usr/bin/xcrun 解决方法: xcode-select --install 安装即可。 |
众所周知,在项目中如果在资源加载请求还未完成的时候,由于阻塞机制,会出现首页白屏的问题,产生很差的用户体验。本文以react为例,提供一个解决方法。
解决原理:使用 onreadystatechange 去监听 readyState,在资源加载完成之前加载一个只有框架的静态页面,页面不请求[……]
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
webpack 3.8.1 使用 extract-text-webpack-plugin 3.0.2 抽取css时失败,报错: ERROR in ./src/static/style/localTime.css Module parse failed: Unexpected token (1:0) You may need an appropriate loader to handle this file type. | .localTimeBox { | color: red; | } @ ./node_modules/style-loader!./src/static/style/localTime.css 4:14-42 webpack-build.config.js 配置为: |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
module: { loaders: [ { test: /\.css$/, loader: ExtractTextPlugin.extract('style-loader', 'style-loader!css-loader', {publicPath: '../'}) } ] }, plugins: [ new ExtractTextPlugin('css/bundle.min.css', {allChunks: true}) ] |
解决方法:
将webpack-build.config.js 配置改为:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
module: { loaders: [ { test: /\.css$/, loader: ExtractTextPlugin.extract({ fallback: 'style-loader', use: ['css-loader'], publicPath: '../' }) } ] }, plugins: [ new ExtractTextPlugin('css/bundle.min.css', {allChunks: true}) ] |
问题就解决了。[……]
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react' 报错:Cannot resolve symbol 'Component' Cannot resolve symbol 'PropTypes' 1.解决 Cannot resolve symbol 'Component' 安装依赖:npm install @types/react --save 调用方法:import React, { Component } from 'react' 2.解决 Cannot resolve symbol 'PropTypes' 安装依赖:npm install prop-types --save 调用方法:import PropTypes from 'prop-types' 注:React.PropTypes 自 React v15.5 起已弃用。请使用 prop-types 库代替。 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 |
一、React.createClass 跟 React.Component 的区别在于后者使用了ES6的语法,用constructor构造器来构造默认的属性和状态。 1. React.createClass import React from 'react'; const Contacts = React.createClass({ render() { return ( <div></div> ); } }); export default Contacts; 2.React.Component import React from 'react'; class Contacts extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); } render() { return ( <div></div> ); } } export default Contacts; 二、 Super(props) 调用父类的构造函数,react希望把所有props,state的定义尽量放到父类中进行。 子类必须在constructor方法中调用super方法,否则新建实例时会报错。这是因为子类没有自己的this对象, 而是继承父类的this对象,然后对其进行加工。如果不调用super方法,子类就得不到this对象。 三、容器组件 Container Components 和展示组件 Presentational Components -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 展示组件 | 容器组件 -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 作用 | 描述如何展现(骨架、样式) | 描述如何运行(数据获取、状态更新) -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 直接使用Redux | 否 | 是 -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 数据来源 | props | 监听 Redux state -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 数据修改 | 从 props 调用回调函数 | 向 Redux 派发 actions -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 调用方式 | 手动 | 通常由 React Redux 生成 -------------------------------------------------------------------------- <strong>四、connect([mapStateToProps], [mapDispatchToProps], [mergeProps], [options])</strong> 连接 React 组件与 Redux store。连接操作不会改变原来的组件类,而是返回一个新的已与 Redux store 连接到组件类。 1.[mapStateToProps(state, [ownProps]): stateProps] (Function): 如果定义该参数,组件将会监听 Redux store 的变化。只要 Redux store 发生变化,mapStateToProps函数就会被调用。 该回掉函数必须返回一个纯对象,这个对象与组件的props合并。如果省略了这个参数,组件将不会监听 Redux store。 如果指定了第二个参数 ownProps,则该参数的值为传递到之间的props,而且只要组件接收到新的 props, mapStateToProps也会被调用。 2.[mapDispatchToProps(dispatch, [ownProps]): dispatchProps] (Object or Function): 如果传递的是一个对象,那么每个定义在该对象的函数都将被当作 Redux action creator, 对象所定义的方法名将作为属性名;每个方法将返回一个新的函数,函数中dispatch方法会将action creator的返回值作为参数执行。 这些属性会被合并到组件的 props 中。如果传递的是一个函数,该函数将接收一个 dispatch 函数,然后由你来决定如何返回一个对象, 这个对象通过 dispatch 函数与 action creator 以某种方式绑定在一起(提示:你也许会用到 Redux 的辅助函数 bindActionCreators())。 如果你省略这个 mapDispatchToProps 参数,默认情况下,dispatch 会注入到你的组件 props 中。 如果指定了该回调函数中第二个参数 ownProp该参数的值为传递到组件的 props,而且只要组件接收到新 props,mapDispatchToProps 也会被调用。 3.[mergeProps(stateProps, dispatchProps, ownProps): props] (Function): 如果指定了这个参数,mapStateToProps() 与 mapDispatchToProps() 的执行结果和组件自身的 props 将传入到这个回调函数中。 该回调函数返回的对象将作为 props 传递到被包装的组件中。你也许可以用这个回调函数,根据组件的 props 来筛选部分的 state 数据, 或者把 props 中的某个特定变量与 action creator 绑定在一起。如果你省略这个参数,默认情况下返回 Object.assign({}, ownProps, stateProps, dispatchProps) 的结果。 4.[options] (Object): 如果指定这个参数,可以定制 connector 的行为。 [pure = true] (Boolean): 如果为 true,connector 将执行 shouldComponentUpdate 并且浅对比 mergeProps 的结果, 避免不必要的更新,前提是当前组件是一个“纯”组件,它不依赖于任何的输入或 state 而只依赖于 props 和 Redux store 的 state。默认值为 true。[withRef = false] (Boolean): 如果为 true,connector 会保存一个对被包装组件实例的引用, 该引用通过 getWrappedInstance() 方法获得。默认值为 false。 |